Introduction
Augmented Reality (AR) is one of the most interesting technologies shaping the way we interact with digital information. Unlike virtual reality, which creates an entirely digital world, AR enhances the real world by placing digital elements on top of what we already see.
From mobile apps and smart glasses to education and retail, AR is becoming more common in everyday life. In this guide, we’ll explain how augmented reality works, what technologies make it possible, and where it is used today.
This article is written to help beginners understand AR in simple terms, without technical jargon.
What Is Augmented Reality?
Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that overlays digital content—such as images, animations, or information—onto the real world through a device.
These devices can include:
-
Smartphones
-
Tablets
-
AR glasses
-
Head-mounted displays
When you point your phone camera at a surface and see digital objects appear on your screen as if they are part of the environment, that is AR in action.
The key idea behind AR is simple:
It enhances reality instead of replacing it.
The Core Components of Augmented Reality
For AR to function properly, several technologies work together behind the scenes.
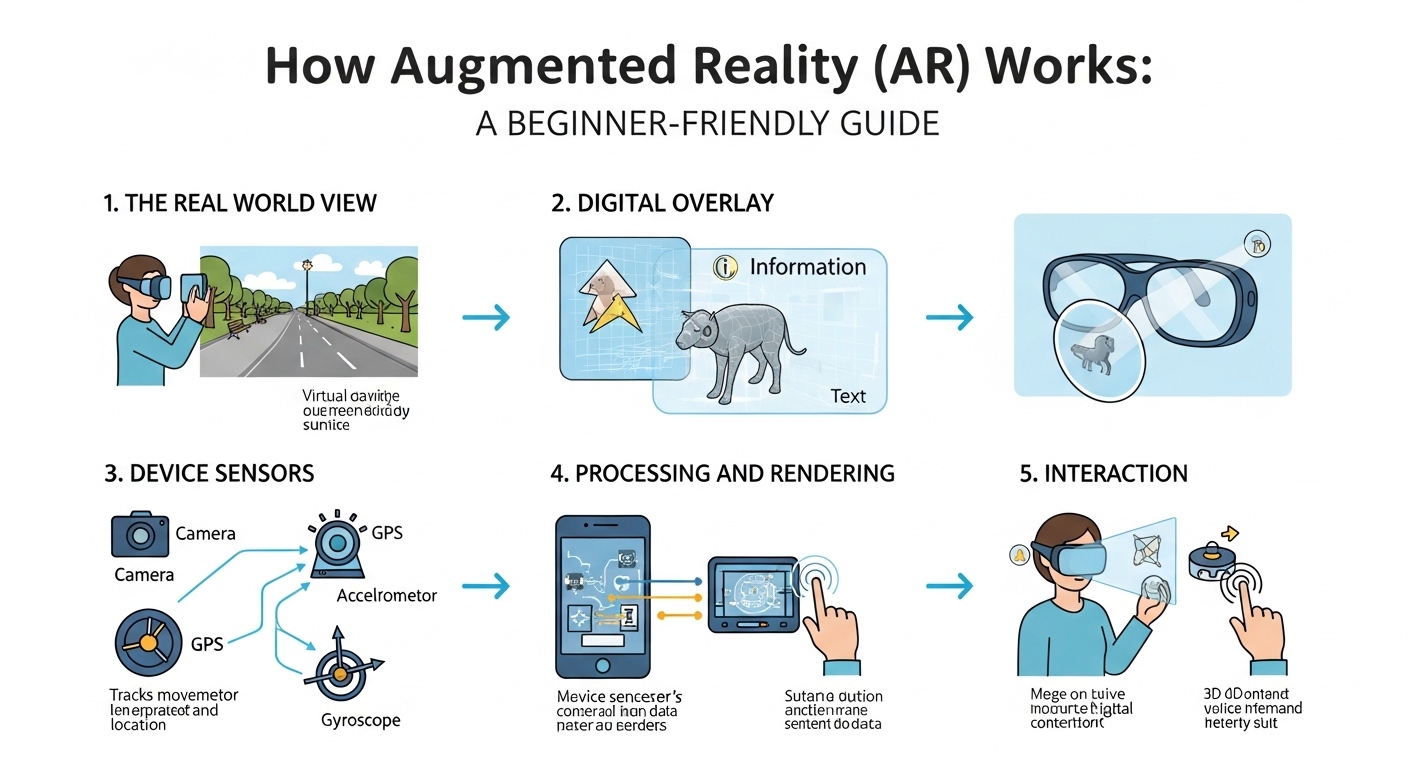
1. Camera and Sensors
The camera captures the real-world environment. Sensors such as:
-
Accelerometers
-
Gyroscopes
-
GPS
help determine the device’s position and orientation. This information allows the AR system to place digital objects correctly in the space.
For example, if you move your phone slightly to the left, the digital object must stay anchored in place. Sensors make that possible.
2. Processing and Software
Once the camera captures the environment, software analyzes the data in real time.
This process includes:
-
Detecting surfaces (walls, floors, tables)
-
Recognizing objects or images
-
Tracking movement
Advanced algorithms calculate where and how digital elements should appear so they look realistic.
Modern smartphones are powerful enough to perform this processing almost instantly.
3. Display Technology
After processing, the system displays the combined image (real world + digital elements) on the screen.
There are two main types of AR display methods:
-
Screen-based AR (most common, used on phones)
-
Optical AR (used in smart glasses, where digital elements appear directly in your field of vision)
The goal is to make the digital objects appear naturally integrated into the physical environment.
How AR Tracks the Real World
One of the most important parts of AR is tracking.
Tracking allows the system to understand:
-
Where the user is
-
What direction the device is facing
-
How the environment is structured
There are two common tracking methods:
Marker-Based AR
This type uses a specific image or QR-like marker.
When the camera detects the marker, digital content appears.
Markerless AR
This more advanced method uses surface detection and environmental understanding instead of markers.
Most modern AR apps use markerless technology.
Real-World Applications of Augmented Reality
AR is no longer limited to experimental projects. It is used across many industries.
Education
Students can interact with 3D models of planets, human anatomy, or historical sites directly from their devices. This can make learning more engaging and interactive.
Retail
Some apps allow users to preview furniture in their home before buying. The digital item appears in the room at scale.
Healthcare Training
Medical students can practice procedures using AR simulations in controlled environments.
Navigation
AR navigation apps overlay arrows and directions directly onto the real-world view through a smartphone camera.
Gaming
AR games combine digital characters with real-world surroundings for immersive experiences.
Augmented Reality vs Virtual Reality
It is common to confuse AR with Virtual Reality (VR), but they are different technologies.
| Augmented Reality (AR) | Virtual Reality (VR) |
|---|---|
| Enhances the real world | Replaces the real world |
| Uses phones or glasses | Uses VR headsets |
| Keeps user aware of surroundings | Fully immersive experience |
AR adds information to your environment, while VR creates a completely separate digital space.
Benefits of Augmented Reality
AR offers several advantages:
-
Enhances learning through visualization
-
Improves customer experience
-
Supports remote collaboration
-
Reduces training risks in certain industries
-
Makes digital information more interactive
Because AR builds on real-world environments, it often feels more natural and accessible than fully immersive technologies.
Limitations and Challenges
While AR has many advantages, there are also challenges:
-
Device compatibility limitations
-
Battery consumption
-
Privacy considerations (camera usage)
-
Environmental detection errors in low-light conditions
As hardware and software improve, many of these limitations are gradually being addressed.
The Future of Augmented Reality
AR technology continues to evolve. Improvements in artificial intelligence, computer vision, and wearable devices are expanding its possibilities.
Future developments may include:
-
Lightweight AR glasses for everyday use
-
More realistic digital object rendering
-
Enhanced workplace collaboration tools
-
Expanded educational applications
While AR is still developing, its practical use is growing steadily.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is augmented reality safe to use?
AR applications are generally safe when used responsibly. However, users should remain aware of their surroundings, especially when moving.
Do you need special equipment for AR?
Most modern smartphones support basic AR features. Advanced experiences may require dedicated AR glasses or headsets.
Is AR only used for gaming?
No. AR is used in education, retail, healthcare training, navigation, and industrial applications.
Does AR store personal data?
Some AR applications may collect usage data. Always review an app’s privacy policy before use.
Conclusion
Augmented Reality works by combining camera input, sensors, real-time processing, and display technology to overlay digital information onto the physical world. Unlike virtual reality, AR enhances your environment rather than replacing it.
