Introduction
Blockchain technology is one of the most talked-about innovations in recent years. While it is often associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, blockchain has many other applications across finance, supply chain, healthcare, and more.
In this guide, we’ll explain the basics of blockchain technology, how it works, its key components, and practical applications. This article is educational, neutral, and designed for beginners who want a clear understanding.
H2: What Is Blockchain Technology?
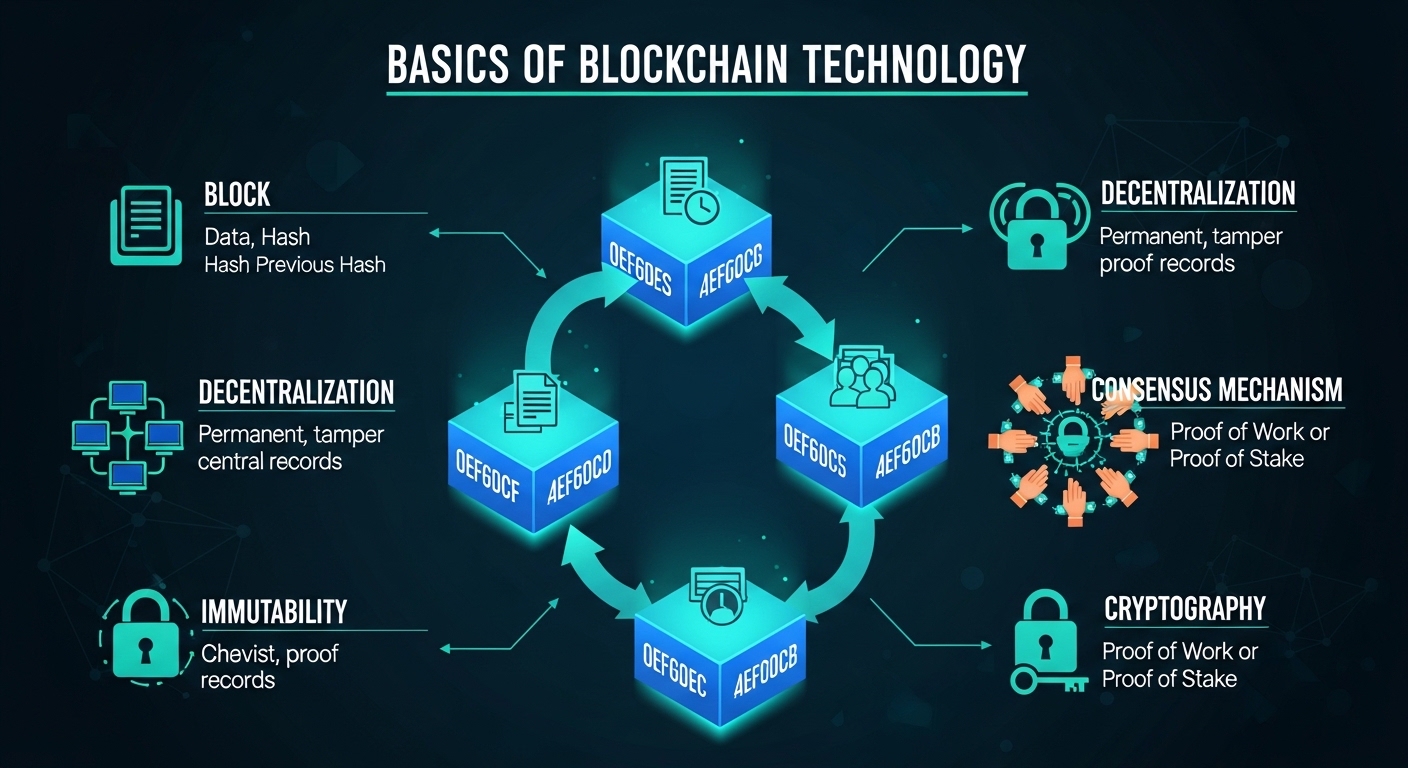
Blockchain is a digital ledger that records information across multiple computers in a way that makes it secure, transparent, and nearly impossible to alter.
Key characteristics include:
-
Decentralization: No single entity controls the data.
-
Transparency: All participants can view the records.
-
Security: Transactions are encrypted and verified by the network.
Unlike traditional databases, blockchain stores data in blocks, which are linked together to form a chain, hence the name. Once information is added, it cannot easily be changed, making it reliable for record-keeping.
H2: How Blockchain Works
Blockchain works through a combination of cryptography, consensus mechanisms, and distributed networks. Here’s a simplified explanation:
-
Transaction Initiation: A user requests a transaction, such as transferring data or assets.
-
Verification: The network of computers (nodes) validates the transaction using specific consensus rules.
-
Block Creation: Once verified, the transaction is grouped with others into a “block.”
-
Block Addition: The new block is added to the existing chain in chronological order.
-
Permanent Record: The transaction becomes a permanent, unchangeable part of the blockchain.
H2: Key Components of Blockchain
Understanding blockchain requires knowing its main elements:
-
Blocks: Containers of transaction data, timestamped and linked to previous blocks.
-
Nodes: Computers that maintain and verify the blockchain network.
-
Cryptography: Secures transactions using advanced mathematical algorithms.
-
Consensus Mechanisms: Methods (like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake) to agree on transaction validity.
-
Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts that run automatically when conditions are met.
Advantages of Blockchain
Blockchain technology offers several benefits:
-
Security: Transactions are encrypted and tamper-resistant.
-
Transparency: Everyone on the network can see the transaction history.
-
Efficiency: Reduces the need for intermediaries in processes.
-
Traceability: Excellent for supply chain management or auditing.
-
Cost Reduction: Eliminates many middlemen and administrative fees.
Common Applications of Blockchain
Blockchain is no longer limited to cryptocurrency. Some practical uses include:
-
Finance & Banking: Secure cross-border payments, fraud prevention, and digital assets.
-
Supply Chain: Track products from origin to delivery, ensuring transparency.
-
Healthcare: Secure patient records and improve data sharing between providers.
-
Voting Systems: Transparent and tamper-proof election systems.
-
Digital Identity: Protect personal data and identity verification.
Limitations to Consider
While blockchain is powerful, it has limitations:
-
Energy Consumption: Some blockchains (like Bitcoin) require high electricity use.
-
Scalability Issues: Handling many transactions at once can be slow.
-
Regulatory Uncertainty: Laws and regulations vary by country.
-
Complexity: Understanding and implementing blockchain can be challenging.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is a revolutionary way to store and share information securely. By understanding its basic principles, key components, advantages, and applications, beginners can appreciate its potential beyond cryptocurrencies.
Whether you are curious about technology, finance, or digital innovation, knowing the basics of blockchain technology is a valuable skill for the modern world.
FAQ (Optional for SEO & AdSense Boost)
Q1: Is blockchain the same as Bitcoin?
A1: No. Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency that uses blockchain, but blockchain can be applied in many other fields like finance, healthcare, and supply chains.
Q2: Can blockchain be hacked?
A2: While highly secure, no system is 100% immune. However, the decentralized and encrypted nature of blockchain makes hacking extremely difficult.
Q3: What is a smart contract?
A3: A smart contract is a self-executing program on the blockchain that runs automatically when certain conditions are met.
Q4: Do I need technical knowledge to understand blockchain?
A4: Basic understanding of digital transactions is enough to grasp blockchain basics. Advanced applications may require more technical knowledge.
