Introduction
Mobile networks have evolved rapidly over the past few decades. From basic voice calls on early cellular systems to high-speed internet streaming on smartphones, each generation of wireless technology has introduced major improvements. Today, 5G technology represents the fifth generation of mobile networks, offering faster speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity than previous generations.
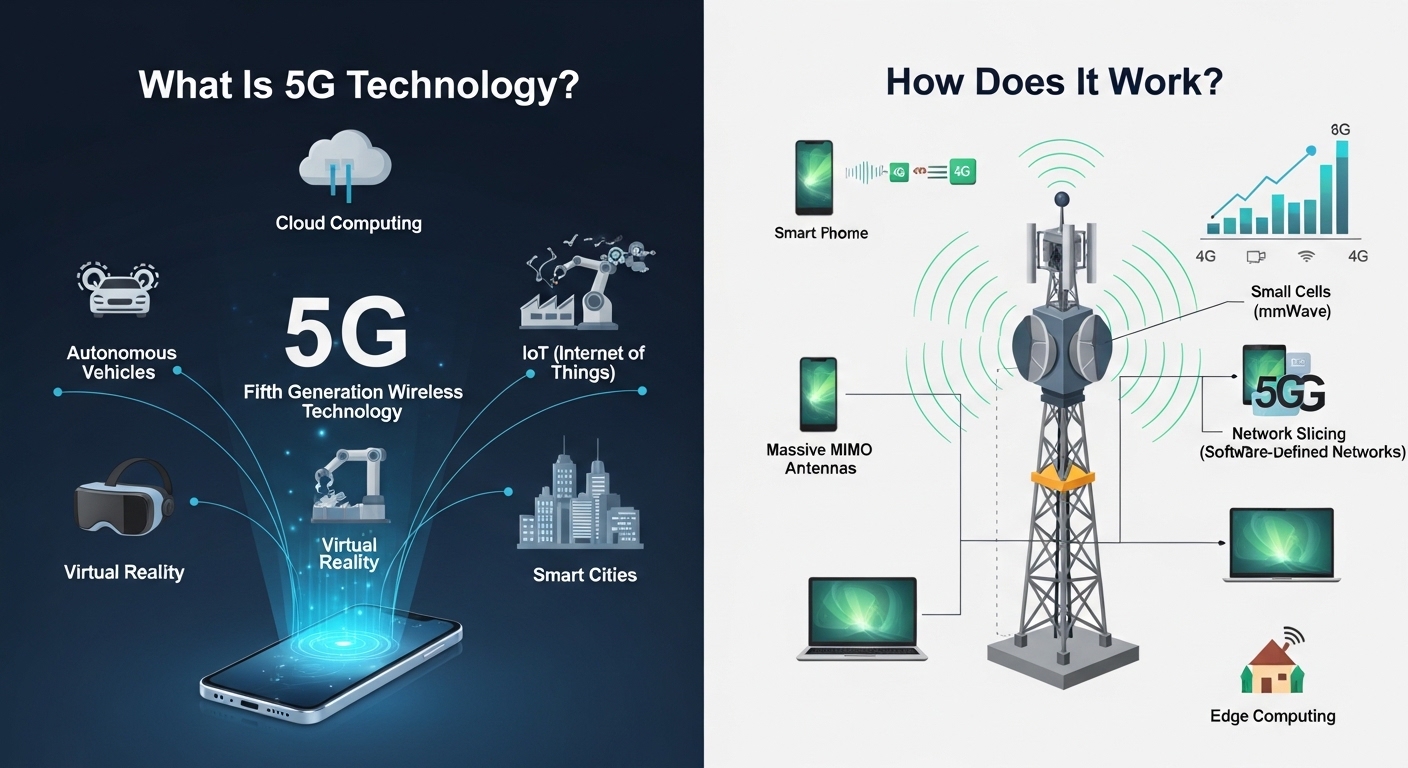
In this guide, we’ll explain what 5G technology is, how it works, its main features, benefits, and potential challenges, all in simple and clear terms.
What Is 5G Technology?
5G stands for fifth-generation wireless network technology. It is the latest standard for mobile communication, designed to connect not only smartphones but also a wide range of devices such as:
-
Smart home systems
-
Wearable devices
-
Industrial machines
-
Autonomous vehicles
-
Internet of Things (IoT) devices
Unlike earlier generations that mainly focused on improving speed, 5G aims to create a more connected and responsive digital environment.
How Did We Get to 5G? (A Quick Evolution Overview)
Understanding 5G becomes easier when we look at earlier generations:
-
2G introduced digital voice calls and text messaging.
-
3G enabled mobile internet access.
-
4G LTE significantly improved internet speeds, allowing HD streaming and video calls.
-
5G expands on these capabilities with higher speed, lower delay, and support for millions of connected devices.
Each generation improved performance, but 5G is designed to support a fully connected digital ecosystem.
How Does 5G Technology Work?
5G operates using radio waves, similar to previous mobile networks. However, it introduces several technological improvements.
1. Higher Frequency Bands
5G uses a wider range of frequency bands, including:
-
Low-band spectrum – Wide coverage but moderate speed
-
Mid-band spectrum – Balanced speed and coverage
-
High-band (millimeter wave) – Extremely fast speeds but shorter range
These multiple layers allow 5G networks to balance speed and coverage effectively.
2. Small Cell Infrastructure
Because high-frequency signals travel shorter distances, 5G networks use small cell stations placed closer together in urban areas. These smaller transmitters help maintain strong, consistent connections.
3. Massive MIMO (Multiple Input, Multiple Output)
Massive MIMO uses multiple antennas at base stations to:
-
Send and receive more data simultaneously
-
Increase network capacity
-
Improve signal efficiency
This allows more users to connect at the same time without slowing down the network.
4. Beamforming Technology
Beamforming directs signals toward specific devices instead of broadcasting signals in all directions. This:
-
Improves connection quality
-
Reduces interference
-
Enhances energy efficiency
Key Features of 5G
5G technology is built around three main performance improvements:
1. Faster Speeds
5G can deliver significantly faster data speeds compared to 4G, making activities like:
-
Streaming high-resolution video
-
Downloading large files
-
Online gaming
much smoother and more efficient.
2. Lower Latency
Latency refers to the delay between sending and receiving data. 5G reduces this delay dramatically, which is important for:
-
Real-time video communication
-
Remote-controlled machinery
-
Online gaming
-
Smart transportation systems
3. Greater Device Capacity
5G networks can support a much larger number of connected devices in a small area. This is essential for:
-
Smart cities
-
IoT networks
-
Industrial automation
Benefits of 5G Technology
5G offers advantages for individuals, businesses, and industries.
For Consumers
-
Faster internet on mobile devices
-
Improved video streaming quality
-
More stable connections in crowded areas
For Businesses
-
Enhanced remote collaboration
-
Support for advanced technologies like AI and IoT
-
Improved cloud computing performance
For Industries
-
Smarter manufacturing systems
-
Real-time monitoring and automation
-
More efficient logistics and transportation
Potential Challenges of 5G
Although 5G provides many benefits, there are also challenges:
1. Infrastructure Costs
Building new towers and small cell networks requires significant investment.
2. Limited High-Band Coverage
Millimeter wave frequencies offer high speeds but have shorter range and may struggle to penetrate buildings.
3. Device Compatibility
Not all devices support 5G. Users may need newer smartphones or hardware to access full 5G capabilities.
Is 5G Safe?
5G technology operates within internationally regulated radio frequency guidelines. It uses non-ionizing radiation, similar to previous mobile networks and Wi-Fi systems. Regulatory authorities set exposure limits to ensure public safety.
The Future of 5G
5G is expected to continue expanding globally. As infrastructure improves, it may support:
-
Smarter cities
-
Autonomous transportation systems
-
Advanced telemedicine applications
-
Improved virtual and augmented reality experiences
In the long term, 5G serves as a foundation for future wireless innovations.
Conclusion
5G technology represents a significant advancement in wireless communication. By offering faster speeds, lower latency, and support for more connected devices, it enables new possibilities for consumers, businesses, and industries.
While infrastructure and compatibility challenges remain, 5G continues to shape the future of digital connectivity. Understanding how it works helps individuals and organizations make informed decisions about adopting new technologies.
FAQ
What does 5G stand for?
5G stands for fifth-generation mobile network technology.
Is 5G faster than 4G?
Yes, 5G generally provides higher speeds and lower latency compared to 4G networks.
Do I need a new phone to use 5G?
Yes, your device must be 5G-compatible to access 5G networks.
Does 5G replace Wi-Fi?
No, 5G and Wi-Fi serve different purposes. They can complement each other rather than replace one another.
