Introduction
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is often called the brain of the computer. It processes instructions, performs calculations, and controls the flow of information inside the computer. Without a CPU, your computer, laptop, or even smartphone would not be able to operate.
What Is a CPU?
A CPU (Central Processing Unit) is a hardware component that executes program instructions. It interprets data from software, performs calculations, and communicates with other components like memory and storage.
Key functions of a CPU include:
-
Executing instructions from programs
-
Performing arithmetic and logical operations
-
Controlling communication between hardware components
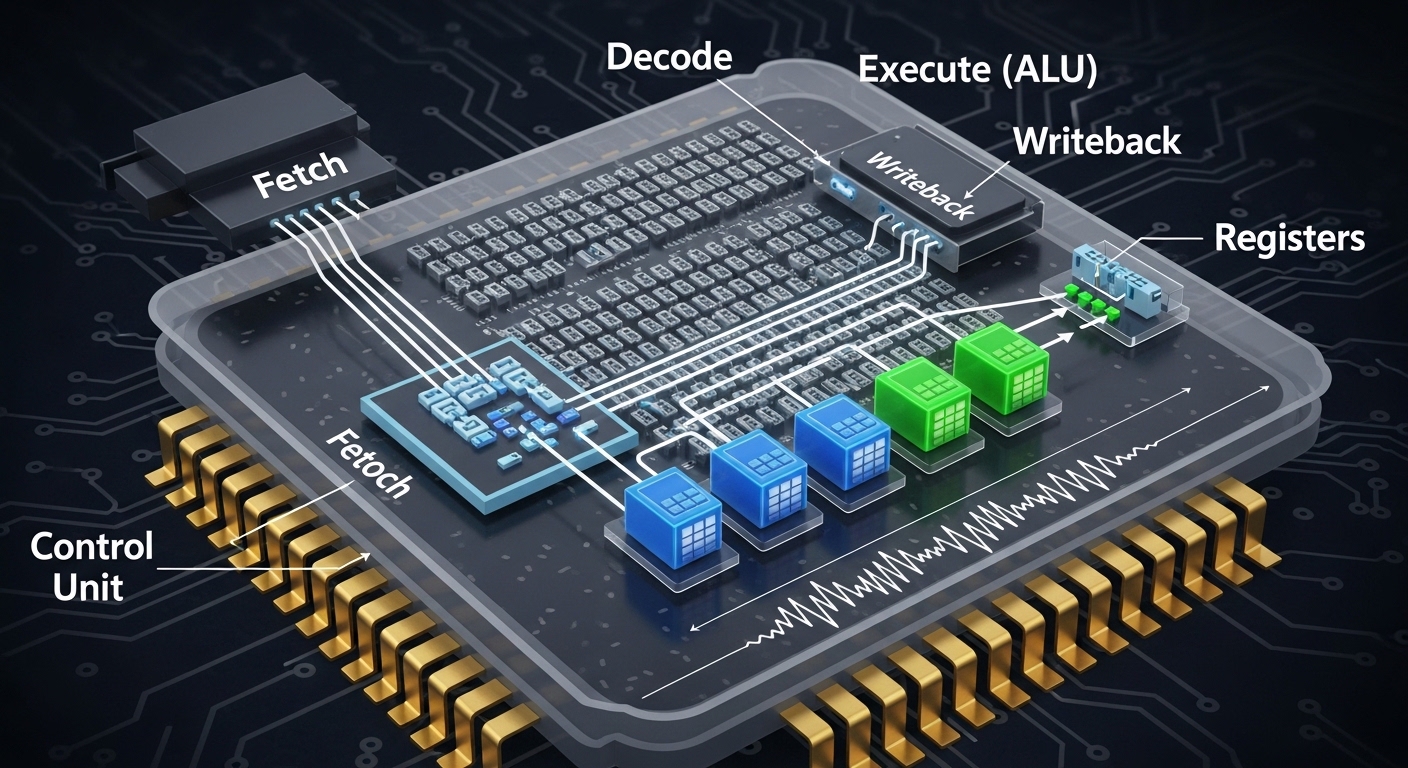
Main Components of a CPU
Control Unit (CU)
The Control Unit manages how data moves inside the CPU. It:
-
Directs instructions to the correct part of the CPU
-
Coordinates communication between memory, input/output devices, and the Arithmetic Logic Unit
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
The ALU handles calculations and logic operations, such as:
-
Addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division
-
Comparing numbers and making logical decisions
Registers
Registers are small, high-speed storage locations inside the CPU. They temporarily hold:
-
Data being processed
-
Instructions currently being executed
Cache Memory
Cache is fast internal memory that stores frequently used data to speed up processing. It reduces the need to access slower main memory (RAM).
How a CPU Processes Instructions
A CPU processes instructions using a simple cycle called the Fetch-Decode-Execute cycle:
-
Fetch – The CPU retrieves an instruction from memory.
-
Decode – The instruction is interpreted by the Control Unit.
-
Execute – The ALU performs calculations or logic, and the result is stored in registers or memory.
This cycle happens millions or even billions of times per second in modern CPUs.
CPU Performance Factors
Several factors affect CPU performance:
-
Clock Speed: Measured in GHz, higher speed means faster instruction processing.
-
Number of Cores: More cores allow simultaneous processing of multiple tasks.
-
Cache Size: Larger cache reduces the time spent accessing data from RAM.
-
Architecture: Modern CPUs have advanced architectures for efficiency, energy saving, and multitasking.
Types of CPUs
-
Single-Core CPU: Handles one task at a time (older computers).
-
Multi-Core CPU: Multiple cores for multitasking (modern computers).
-
Server CPUs: Designed for high-speed data processing and multiple simultaneous users.
-
Mobile CPUs: Optimized for low power consumption in laptops and smartphones.
Why the CPU Is Important
The CPU determines:
-
Speed of your computer
-
Ability to run multiple applications
-
Efficiency in gaming, video editing, and scientific calculations
A better CPU usually leads to faster and smoother computing experiences.
Conclusion
CPUs are the heart of every computer, responsible for executing instructions and managing data flow. Understanding how they work can help you choose the right CPU for your needs and appreciate the complexity behind modern computing.
By knowing the components, processing cycle, and performance factors, anyone can gain a solid understanding of this critical technology.
FAQ
Q1: What does CPU stand for?
A1: CPU stands for Central Processing Unit, which acts as the brain of the computer.
Q2: How does a CPU communicate with other parts of a computer?
A2: The CPU communicates through the bus system, which connects memory, storage, and input/output devices.
Q3: What is the difference between CPU cores and threads?
A3: Cores are individual processing units inside a CPU, while threads are virtual pathways that allow cores to handle multiple tasks simultaneously.
Q4: Can a computer run without a CPU?
A4: No, the CPU is essential; without it, the computer cannot process instructions or operate.
