Introduction
Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming increasingly popular as people look for cleaner alternatives to traditional petrol-powered cars. A key part of this transition is EV charging stations, which provide the energy needed to power these vehicles.
In this guide, we’ll explain how EV charging stations work, the types available, and how renewable energy supports them. This is purely educational and helps readers understand the technology behind modern EV infrastructure.
What is an EV Charging Station?
An EV charging station is a device that supplies electric energy to recharge electric vehicles. They are installed in public locations, workplaces, and homes.
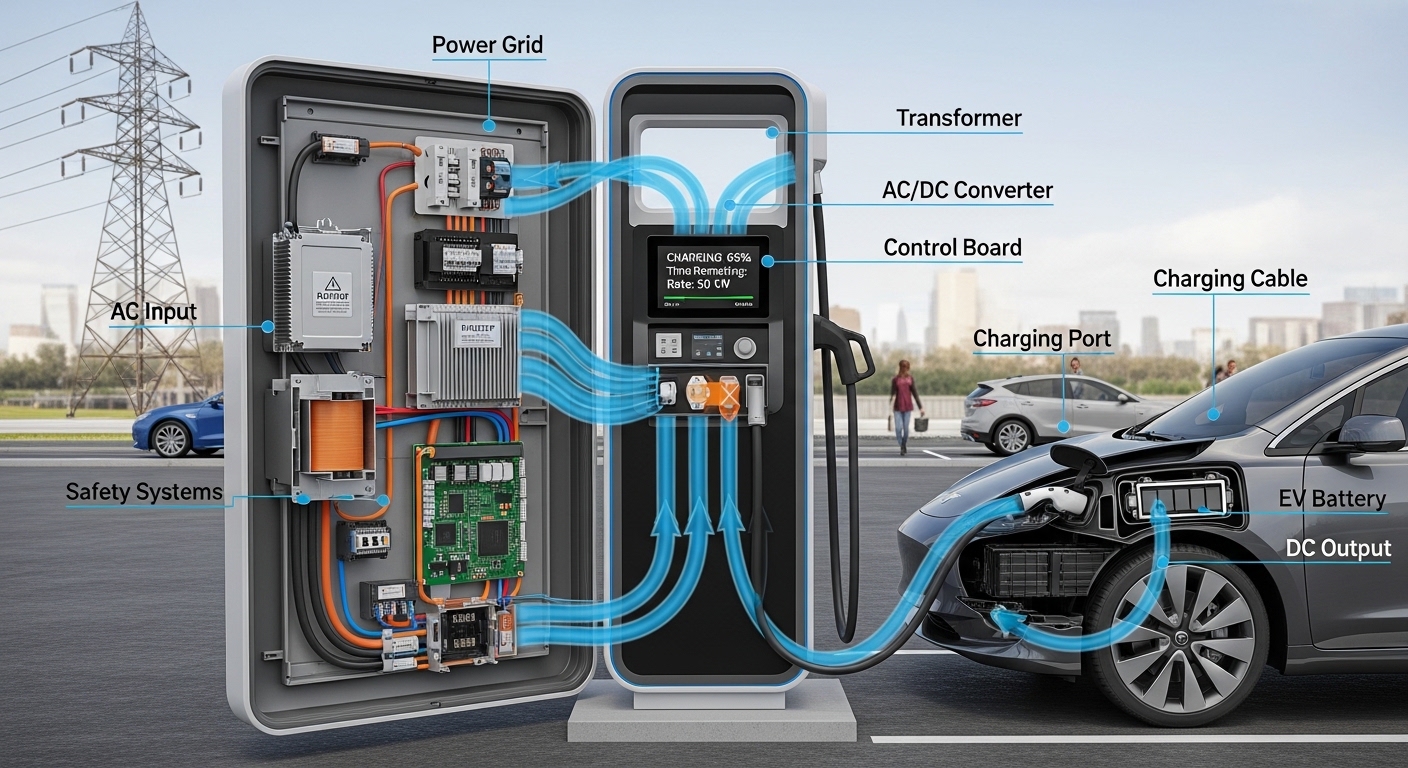
Main components of a charging station include:
-
Charging plug and cable – connects the station to the vehicle
-
Control system – manages charging speed and safety
-
Power supply – sourced from the electrical grid or renewable energy sources
-
Communication module – allows monitoring, billing, and usage tracking
Types of EV Charging Stations
EV charging stations are classified by how quickly they charge a vehicle and how they connect to the grid.
1. Level 1 Charging (Slow Charging)
-
Uses a standard household outlet (120V)
-
Adds about 3–5 miles of range per hour
-
Ideal for overnight home charging
2. Level 2 Charging (Medium-Speed Charging)
-
Requires a 240V outlet (similar to home appliances like ovens)
-
Adds 15–30 miles of range per hour
-
Common in homes, offices, and public locations
3. DC Fast Charging (Rapid Charging)
-
Uses direct current (DC) instead of alternating current (AC)
-
Can charge a vehicle to 80% in 20–60 minutes
-
Found in highways and commercial stations
How Charging Works
The process of charging an EV is straightforward:
-
Plugging In: The user connects the vehicle to the station using a compatible connector.
-
Authentication (Optional): Some public stations require an app or card to start charging.
-
Power Flow: Electricity flows from the station to the vehicle’s battery.
-
Monitoring: The charging system monitors voltage, current, and battery level to ensure safety.
-
Completion: Once the battery is full or the desired level is reached, the system stops automatically.
Renewable Energy Integration
Many modern EV charging stations are connected to renewable energy sources, such as:
-
Solar panels – generate electricity on-site
-
Wind energy – supplies power through the grid
-
Battery storage systems – store renewable energy for peak use
Benefits of using renewable energy:
-
Reduces carbon footprint
-
Supports sustainable energy adoption
-
Helps stabilize grid demand
Safety Features
EV charging stations include several safety mechanisms:
-
Overcurrent protection
-
Ground fault detection
-
Temperature monitoring
-
Emergency shut-off
These features ensure that charging is safe for both the vehicle and the user.
Tips for Using EV Charging Stations
-
Check compatibility: Ensure your vehicle connector matches the station type.
-
Plan ahead: Use apps to find nearby charging stations during travel.
-
Avoid peak hours: Public stations can be busy during commute times.
-
Follow instructions: Each station may have slightly different usage steps.
Conclusion
EV charging stations are a critical component of the electric vehicle ecosystem. Understanding how they work, the types available, and how renewable energy can be integrated helps users and enthusiasts appreciate the technology behind cleaner transportation.
By following proper usage and safety practices, EV owners can efficiently charge their vehicles while supporting sustainable energy adoption.
FAQ
Q1: How long does it take to charge an EV?
A1: Charging time depends on the station type and battery size. Level 1 takes hours, Level 2 takes a few hours, and DC fast chargers can provide 80% charge in 20–60 minutes.
Q2: Can I charge my EV at home?
A2: Yes, Level 1 and Level 2 charging stations are commonly installed at homes.
Q3: Are EV charging stations safe?
A3: Yes, all charging stations have built-in safety features like overcurrent protection and ground fault detection.
Q4: Can renewable energy fully power an EV?
A4: Yes, when charging stations are connected to solar or wind energy systems, they can supply electricity entirely from renewable sources.
