Introduction
Solar energy is one of the fastest-growing renewable energy sources in the world. Solar panels allow us to convert sunlight into usable electricity, providing a clean and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
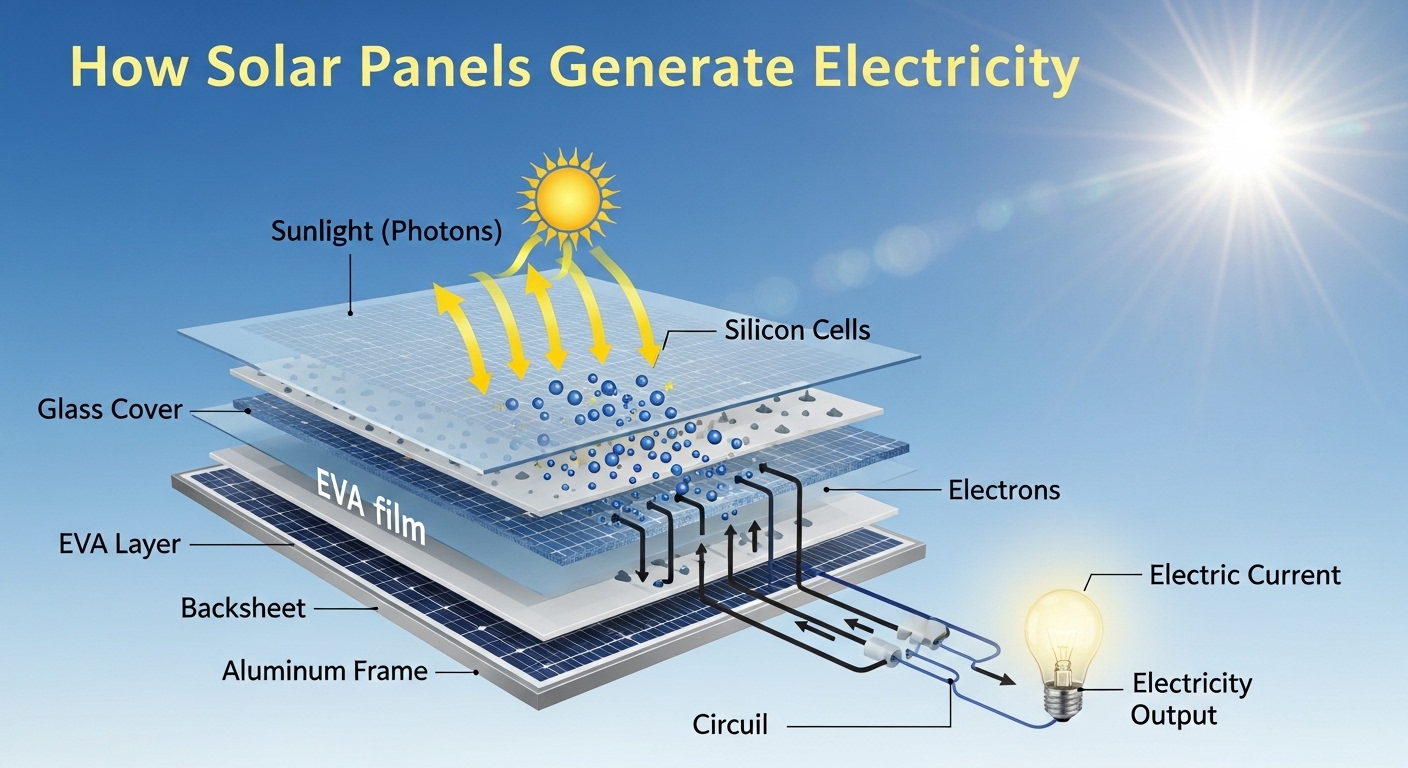
In this guide, we will explain how solar panels work, the main components, and the process of converting sunlight into electricity, in a way that anyone can understand—even beginners.
What Are Solar Panels?
Solar panels, also called photovoltaic (PV) panels, are devices that capture sunlight and convert it into electrical energy. They are made up of multiple solar cells, which are the core units responsible for producing electricity.
Key features of solar panels include:
-
Durability: Panels are designed to withstand weather conditions.
-
Efficiency: Modern panels convert a significant portion of sunlight into energy.
-
Longevity: High-quality panels can last 25–30 years with proper care.
Components of a Solar Panel System
A typical solar panel system consists of several important components:
-
Solar Cells – Made of silicon, these cells absorb sunlight and generate electrical charges.
-
Glass Layer – Protects the cells while allowing sunlight to pass through.
-
Frame – Usually aluminum, it provides support and durability.
-
Inverter – Converts the direct current (DC) electricity from solar cells into alternating current (AC) used by homes and businesses.
-
Mounting System – Holds the panels in place on rooftops or the ground.
-
Wiring – Connects the panels to the inverter and electrical system.
How Solar Panels Convert Sunlight into Electricity
The process of generating electricity involves several steps:
-
Sunlight Absorption – Solar cells absorb photons (light particles) from the sun.
-
Electron Excitation – The energy from photons knocks electrons in the silicon cells loose, creating a flow of electric current.
-
Direct Current (DC) Production – The movement of electrons generates DC electricity.
-
Inversion to AC – An inverter converts DC into AC electricity, which can be used in homes or sent to the electrical grid.
-
Distribution – Electricity powers appliances, lights, and other devices.
Benefits of Solar Electricity
Solar electricity provides several practical and environmental benefits:
-
Renewable Source: Sunlight is abundant and free.
-
Reduces Energy Bills: Generates electricity for personal or business use.
-
Low Maintenance: Solar panels require minimal upkeep once installed.
-
Environmentally Friendly: Reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels.
-
Scalable: Can be used for small residential systems or large solar farms.
Common Misconceptions
Some common misunderstandings about solar panels include:
-
“Solar panels only work on sunny days.”
→ Panels still generate electricity on cloudy days, though less efficiently. -
“They are very expensive.”
→ Prices have decreased significantly over the past decade, making them affordable for many households. -
“Maintenance is complicated.”
→ Regular cleaning and inspection are usually enough to keep panels functioning well.
Tips for Maximizing Solar Efficiency
To get the most out of solar panels, consider these tips:
-
Optimal Placement: Position panels to face the sun’s path (usually south-facing in the northern hemisphere).
-
Avoid Shading: Keep panels free from trees, chimneys, or other obstacles.
-
Regular Cleaning: Remove dust, leaves, and debris for maximum sunlight absorption.
-
Professional Inspection: Have a technician check the system periodically.
Conclusion
Solar panels are a remarkable technology that turns sunlight into usable electricity through a simple yet powerful process. By understanding how solar cells work, the components involved, and the steps to maximize efficiency, anyone can appreciate the role of solar energy in creating a cleaner and more sustainable future.
FAQ
Q1: How long do solar panels last?
A1: Most modern solar panels last 25–30 years with proper maintenance.
Q2: Do solar panels work at night?
A2: No, panels generate electricity from sunlight, but energy storage systems like batteries can store daytime energy for nighttime use.
Q3: Can solar panels power an entire home?
A3: Yes, with enough panels and storage, they can provide full electricity needs, depending on energy consumption and sunlight availability.
Q4: Are solar panels environmentally safe?
A4: Yes, they produce clean energy, significantly reducing carbon emissions compared to traditional power sources.
