Introduction
Electric motors are at the heart of countless devices, from household appliances to industrial machines and electric vehicles. Understanding how electric motors work is essential for anyone interested in technology or engineering.
In this guide, we will explain the principles behind electric motors, the different types, their components, and real-world applications—all in a clear, easy-to-understand format.
What Is an Electric Motor?
An electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. This mechanical energy is then used to perform work, such as spinning a fan, driving a machine, or powering a vehicle.
Key points about electric motors:
-
They rely on electromagnetic principles.
-
They come in various sizes, from tiny motors in electronics to massive motors in factories.
-
Efficiency depends on the design, type, and materials used.
How Electric Motors Work – The Basics
Electric motors operate based on the interaction between magnetic fields and electric currents. The main idea is:
-
Electric current passes through a coil or wire.
-
The current generates a magnetic field.
-
This magnetic field interacts with permanent magnets or another magnetic field.
-
The interaction produces rotational motion, which is mechanical energy.
This process happens continuously in a loop, which keeps the motor spinning.
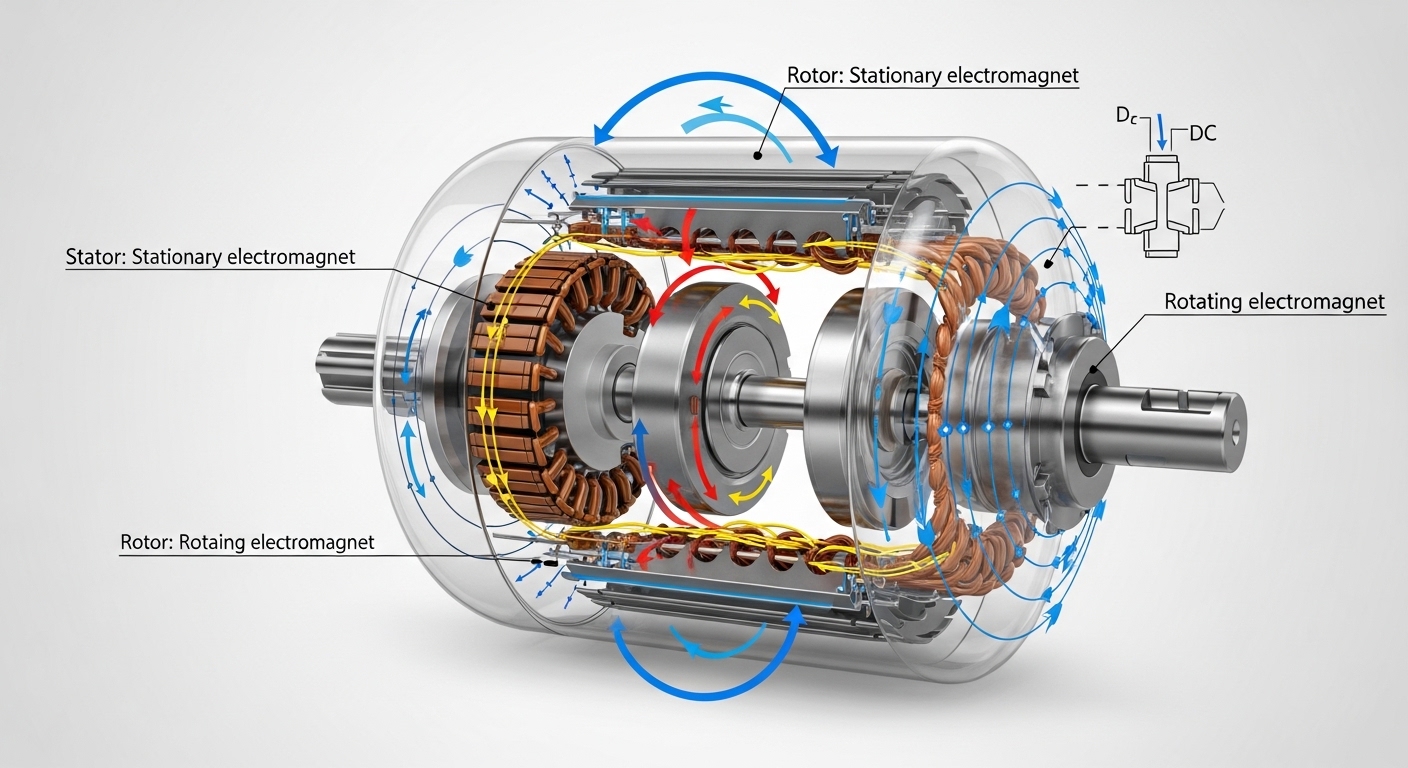
Key Components of an Electric Motor
Understanding the parts of a motor helps you see how it works. The main components include:
-
Stator: The stationary part of the motor that generates a magnetic field.
-
Rotor: The rotating part connected to the output shaft that produces motion.
-
Commutator (in DC motors): Reverses the direction of current to keep the rotor spinning.
-
Windings or Coils: Conduct electricity and create the magnetic field.
-
Bearings: Reduce friction and support smooth rotation.
-
Housing: Protects the motor components from dust, debris, and damage.
Types of Electric Motors
There are many types of electric motors, but the most common are:
1. DC Motors
-
Powered by direct current (DC).
-
Simple design, easy to control.
-
Used in toys, small appliances, and automotive systems.
2. AC Motors
-
Powered by alternating current (AC).
-
Common in household appliances and industrial machines.
-
Can be split into synchronous and asynchronous (induction) motors.
3. Brushless Motors
-
No brushes, reducing maintenance.
-
High efficiency and long lifespan.
-
Common in drones, electric cars, and computer fans.
Applications of Electric Motors
Electric motors are everywhere. Some everyday applications include:
-
Fans, heaters, and air conditioners
-
Washing machines and refrigerators
-
Electric vehicles (cars, scooters, bikes)
-
Industrial machines (conveyors, pumps, compressors)
-
Robotics and automation systems
Advantages of Electric Motors
-
Energy efficiency: Convert electricity to motion efficiently.
-
Low maintenance: Especially brushless designs.
-
Versatility: Can power small gadgets to massive industrial equipment.
-
Environmentally friendly: Produce no direct emissions when used in electric vehicles.
Tips for Using and Maintaining Electric Motors
Proper care ensures longevity and efficiency:
-
Regularly inspect for dust and debris buildup.
-
Lubricate bearings as recommended by the manufacturer.
-
Avoid overloading the motor beyond its rated capacity.
-
Check electrical connections to prevent overheating.
-
Use motors in a dry and ventilated environment to reduce wear.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
-
Using the wrong voltage or current type.
-
Neglecting regular maintenance.
-
Overheating due to excessive load or poor ventilation.
-
Ignoring unusual noises or vibrations.
Conclusion
Electric motors are fundamental to modern life, powering everything from household gadgets to industrial machinery. By understanding how electric motors work, their components, types, and maintenance tips, you can better appreciate this technology and even troubleshoot or select motors for specific applications.
FAQ
Q1: What is the main principle behind electric motors?
A1: Electric motors work on the principle that electric current generates a magnetic field, which interacts with another magnetic field to produce rotational motion.
Q2: What is the difference between AC and DC motors?
A2: AC motors are powered by alternating current, while DC motors use direct current. AC motors are common in appliances, while DC motors are often used in vehicles and small devices.
Q3: How can I extend the life of an electric motor?
A3: Regular maintenance, proper voltage use, correct load, and keeping the motor clean and ventilated are key factors for longevity.
Q4: What are brushless motors used for?
A4: Brushless motors are used in drones, electric cars, computers, and other devices where efficiency and low maintenance are critical.
